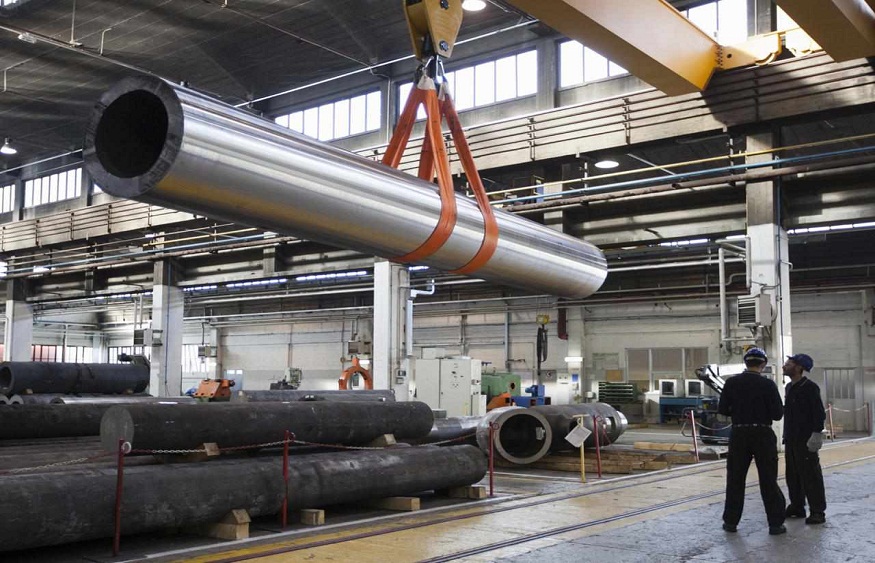
When it comes to investing in exchange-traded funds (ETFs), the broad categories can sometimes be confusing. Two commonly compared ETFs are Manufacturing ETFs and Industrial ETFs. While these might seem similar on the surface, the subtle differences between them can have significant implications for your investment strategy. Understanding these distinctions can help investors make informed decisions and diversify their portfolios effectively.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between manufacturing ETFs and industrial ETFs, and why it’s important to know which one suits your investment needs.
What Is a Manufacturing ETF?
A Manufacturing ETF is a type of exchange-traded fund that focuses on companies involved in the manufacturing sector. These companies are typically engaged in the production of goods ranging from consumer electronics, automobiles, textiles, chemicals, and even industrial machinery. The manufacturing ETF provides a convenient way for investors to gain exposure to this vital part of the economy without having to select individual stocks.
Invest in manufacturing ETF offers exposure to a diverse range of companies that produce finished goods for both consumer and industrial use. Since these ETFs focus on companies that generate revenue from the production process itself, they provide a unique opportunity to invest in the backbone of global commerce.
What Is an Industrial ETF?
On the other hand, Industrial ETFs tend to be broader in scope. These funds include companies from a wider range of industries that may not just focus on manufacturing but also on sectors like transportation, infrastructure, aerospace, and logistics. While manufacturing companies may still be included in industrial ETFs, they are often a subset of a larger grouping of companies involved in overall industrial production and support services.
Industrial ETFs are designed for investors who want exposure to the broader industrial sector, which may include companies providing services such as construction, defense, energy equipment, and utilities. As such, industrial ETFs are more diversified but less concentrated specifically on manufacturing.
Key Differences Between Manufacturing and Industrial ETFs
- Focus on Core Sector:
- Manufacturing ETFs zero in on companies that are directly involved in producing goods. These funds typically feature firms that specialize in the creation of tangible products, making them more specific in their investment focus.
- Industrial ETFs, in contrast, include a wider array of sectors that may not focus solely on production. These funds encompass industries like logistics, transportation, and energy, along with manufacturing.
- Diversity of Holdings:
- A manufacturing ETF is more focused, meaning it might carry higher risk but also higher potential returns from the manufacturing sector alone.
- An industrial ETF tends to be more diversified across industries, which can make it a safer option for conservative investors but may offer slower growth compared to the more specialized manufacturing ETFs.
- Performance Tied to Different Economic Indicators:
- The performance of manufacturing ETFs is often closely tied to consumer demand and the strength of production capacity. Factors like inflation, supply chain issues, and technological advances directly impact these funds.
- Industrial ETFs, however, are influenced by broader economic trends, including infrastructure spending, government defense contracts, and global energy demand. As a result, industrial ETFs tend to react to a wider array of economic indicators.
- Geographic Considerations:
- A manufacturing ETF might include companies that are more globally distributed, as manufacturing is often an international process. Companies in these funds may have production facilities and supply chains across various countries.
- Meanwhile, industrial ETFs might lean more heavily on domestic companies or sectors within specific regions, especially when it includes industries like defense and utilities that are often tied to local markets.
Conclusion
Whether you choose to invest in a manufacturing ETF or an industrial ETF, both offer valuable opportunities to gain exposure to key sectors of the economy. Understanding the differences between these two types of ETFs is crucial for making informed investment decisions. While manufacturing ETFs provide more specialized exposure to production-focused companies, industrial ETFs offer broader exposure to the entire industrial sector. Consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and the economic indicators driving these sectors before making your choice.